What is Hearing Loss?
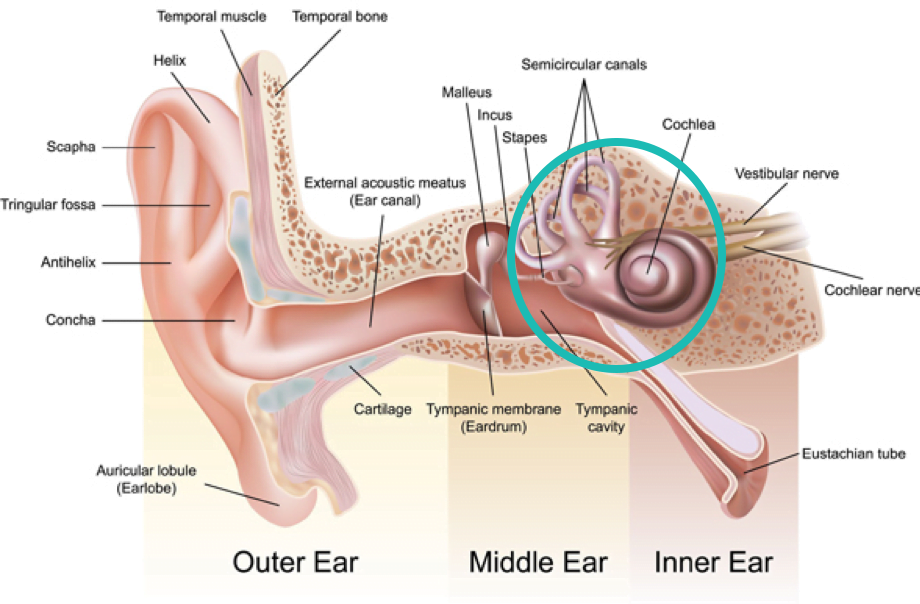
Hearing loss is a decreased ability to hear sounds, ranging from mild to profound. 1 in 6 New Zealanders have hearing loss and there are many ways that can cause hearing loss. This can occur in one or both ears and can be caused by various factors, including aging, exposure to loud noises, certain medical conditions, and genetic factors. Hearing loss can affect a person's ability to communicate and enjoy daily activities and may require hearing aids or cochlear implants for treatment. Hearing loss can be permanent, temporary or a mixture of both. Depending on the site of the lesion, different management are required.
Through a hearing test, we can find out if the present hearing loss is sensorineural, conductive and mixed hearing loss. Depending on the type of hearing loss we can provide hearing rehabilitation through hearing aids or referral to ENT for medical management.
Some conditions require other medical professionals promptly, so if you are unsure if your condition is serious, please get in touch with the audiologist quickly.
There are three types of hearing loss
Sensorineural Hearing loss
Damage to inner ear cells in the cochlea (Hearing organ) or hearing nerve is the cause. The change is not normally reversible except on certain occasions.
Illness
Ototoxic drugs (Oto - ear | Toxic - Toxic - Toxic to ear)
Normal aging process
Head trauma
Noise Exposure - Acutely or Chronically
Hereditary Factor
Ischemic
Management
Cannot be reversed
In the case of sudden sensorineural hearing loss, taking Prednisone (Steroid) in a timely manner may reverse the hearing loss
Hearing rehabilitation using hearing aids
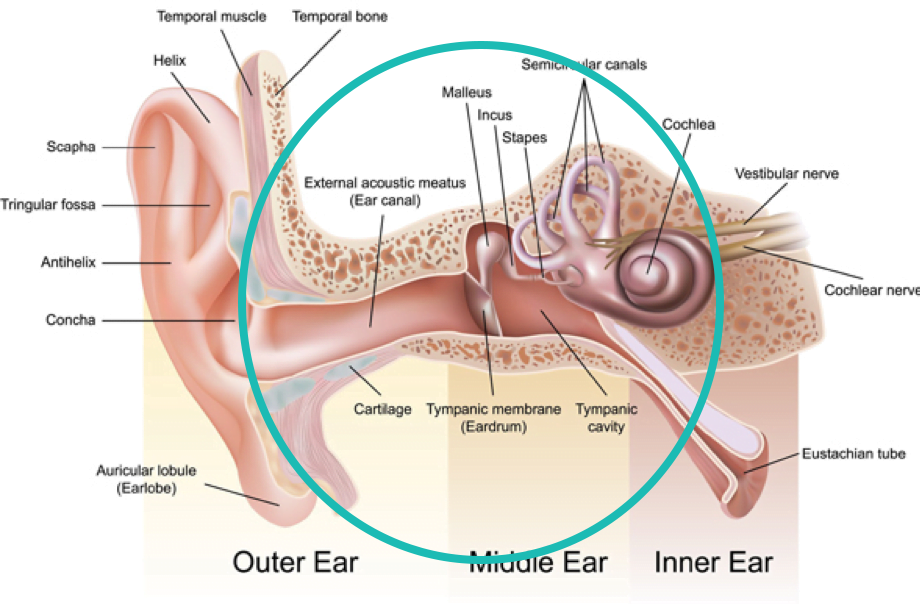
Conductive Hearing loss
Blockage of the ear canal or disruption of movements or middle ear structures
Ear wax or foreign body obstructing the ear canal
Middle ear or outer ear infection
Fluid in the middle
Perforated eardrum
Eustachian tube dysfunction
Cholesteatoma
Severe Exostoses
Abscess or malformation of the outer and middle ear or ear canal
Management
Through consultation with ENT for medical or surgical options
Removing of wax or foreign body
Hearing rehabilitation through hearing aids, if surgery is not recommended
Mixed Hearing loss
A mixture of both sensorineural and conductive hearing loss. Such as
Perforated ear drum with existing sensorineural hearing loss
Wax or foreign body in the ear canal with existing sensorineural hearing loss
Management
Through consultation with ENT for medical or surgical options
Removing of wax or foreign body
Hearing rehabilitation through hearing aids, if surgery is not recommended